Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic illness that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when your body can’t produce or use insulin properly, leading to high blood sugar levels. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications like nerve damage, heart disease, and blindness.
The good news is that diabetes is manageable, but early detection is crucial. In this article, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to get tested for diabetes, including symptoms to watch out for, steps involved in diabetes testing, at-home diabetes testing, the importance of early detection, types of diabetes tests, and tips for adjusting to a diagnosis.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
Diabetes symptoms can be subtle and easy to overlook. However, it’s important to recognize them early to prevent complications.
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Slow healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands/feet
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare professional as soon as possible and ask for a diabetes test. Early detection can help you manage the condition better and prevent complications.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Diabetes Testing
Diabetes testing involves a few simple steps to help determine if you have the condition.
The first step is to book an appointment with your healthcare professional. During the appointment, your healthcare provider will ask you to provide a medical history, including your family’s medical history of diabetes, any symptoms you’ve experienced, and your lifestyle habits.
Once your healthcare provider has gathered the necessary information, they’ll order a diabetes test. There are two main types of diabetes tests: blood glucose tests and A1C tests.
Blood glucose tests provide a snapshot of your blood sugar levels at the time of the test. Your healthcare provider will order a fasting blood glucose test, where you’ll need to avoid eating or drinking anything except water for at least eight hours before the test. In some cases, your healthcare provider may order a random blood glucose test or a glucose tolerance test to confirm a diagnosis.
An A1C test, also known as a glycated hemoglobin test, provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the last two to three months. It does not require fasting.
Before getting tested, it’s important to follow instructions from your healthcare provider for preparation, as different tests may require different preparations. Make sure to ask your healthcare provider for any special instructions ahead of time.
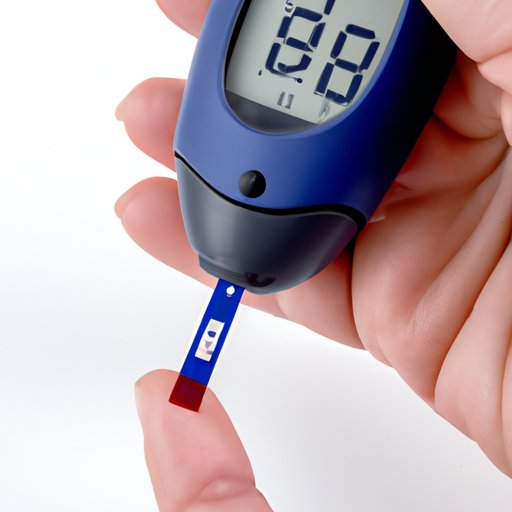
At-Home Diabetes Testing
At-home diabetes testing can be convenient and relatively inexpensive. However, they may not always be as accurate as tests performed by healthcare professionals.
There are two main types of at-home diabetes tests: blood glucose meters and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs).
Blood glucose meters are small, easy-to-use devices that provide a reading of your blood glucose levels using a small drop of blood from your finger. CGMs, on the other hand, use a small sensor or wire that is inserted under the skin to measure your blood glucose levels throughout the day and night.
While at-home testing can be useful for those who need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, it’s important to remember that these tests should be used in conjunction with guidance from a healthcare professional. Always confirm any test results with your healthcare provider and discuss any concerns you may have about them.
The Importance of Early Detection
Undiagnosed diabetes can lead to serious long-term complications that can negatively impact your quality of life. If you develop nerve damage, heart disease, and blindness, it can be difficult to manage these conditions effectively. Catching diabetes early and managing it effectively can help prevent complications from developing.
Managing diabetes may involve a combination of lifestyle changes and medications. Incorporating healthy habits like regular exercise, healthy eating, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce your risk of complications.
If you’ve been diagnosed with diabetes, working with your healthcare provider and a registered dietitian can help you manage your condition effectively. They can provide customized advice on dietary changes, exercise, and medication management to help you reach your goals.
Types of Diabetes Tests
There are several tests that can be used to diagnose diabetes. Your healthcare provider may order one or more of these tests based on your symptoms and individual needs.
The main types of diabetes tests include:
- Blood glucose tests
- A1C tests
- Oral glucose tolerance tests
- Fructosamine tests
Blood glucose tests provide a snapshot of your blood sugar levels at the time of the test. An A1C test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the last two to three months.
An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) involves drinking a sugary solution, then measuring your blood sugar levels before and two hours after drinking it. This test assesses how your body processes glucose over time and is often used to diagnose gestational diabetes.
A fructosamine test measures your average blood sugar level over the last two to three weeks and provides a clearer picture of how effective your diabetes management has been.
Based on your symptoms and individual needs, your healthcare provider will help determine which diabetes test is appropriate for you.
Conclusion
Getting tested for diabetes is an important step in managing the condition effectively. At-home diabetes testing can be convenient, but it’s important to confirm any results with a healthcare professional. Catching diabetes early and taking steps to manage it effectively can help prevent complications from developing. Speak to your healthcare provider if you have any concerns about diabetes testing or managing the condition effectively.
For more information or support, consider reaching out to diabetes organizations or healthcare professionals who specialize in diabetes management.




