Introduction
Arthritis is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and while it can be a painful experience, it can also be a difficult one to diagnose. There are many different types of arthritis, each of which can present unique symptoms and challenges. Without a thorough diagnosis, it can be challenging to manage and treat the condition effectively.
The purpose of this article is to explore whether or not arthritis can be seen on an x-ray. We will examine the limitations of x-rays and other diagnostic techniques and offer tips on how to interpret x-ray results when it comes to detecting this condition.
“Seeing Beyond the X-Ray: Understanding Arthritis Diagnosis Techniques”
X-rays have been used in medicine for over a century, and they remain an essential tool for diagnosing arthritis. However, relying solely on an x-ray can be problematic because x-rays cannot always detect the early signs of arthritis or its full extent.
Other diagnostic methods such as blood tests and physical exams can provide additional information when used in conjunction with an x-ray. A comprehensive approach, including a full medical history, physical exam, imaging, and laboratory tests, is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
“Decoding Your X-Ray Results: Is Arthritis Hiding in Plain Sight?”
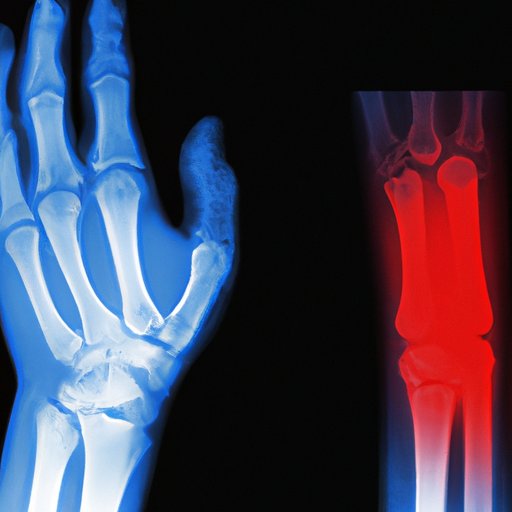
X-rays can identify joint damage and bone spurs, which are typical symptoms of arthritis. However, an x-ray cannot always reveal the full extent of the damage to cartilage and soft tissue. In earlier stages of the condition, it can be challenging to detect arthritis on an x-ray scan.
Knowing how to interpret your x-ray results can help you identify any potential signs of arthritis, such as joint space narrowing, bony lesions, and bone erosion. Your doctor can help you understand what to look for in an x-ray and provide visuals to help you visualize the effects of arthritis in the body.
“The Limitations of Imaging: What Your X-Ray Might Be Missing About Arthritis”
X-rays are limited in terms of what they can reveal about arthritis, which is why healthcare providers may use other diagnostic methods like MRI and ultrasound, which can detect soft tissue damage that may not appear on an x-ray.
Identifying the full extent of the damage is essential, as it helps healthcare providers understand the severity of the condition and what treatment options are best for the patient. A combination of diagnostic methods is often used to diagnose arthritis accurately, particularly in the early stages.
“Spotting Arthritis on an X-Ray: What You Need to Know”
When analyzing an x-ray to detect arthritis, medical professionals typically look for bone spurs, joint space narrowing, or misshapen bones. X-rays can also show changes in bone density, which can be indicative of various types of arthritis like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
However, x-rays are not just useful for detecting arthritis. They are also commonly used to track the progression of the condition over time. Frequent x-rays can help a healthcare provider monitor the patient’s treatment progress and adjust their treatment plan accordingly.
“Beyond the Scan: Understanding Arthritis Diagnostics for a More Accurate Diagnosis”
Arthritis can be a complex condition with various contributing factors, making an accurate diagnosis essential for managing the condition effectively. Along with x-rays, healthcare providers may use blood tests, physical exams, and family medical history to make a more accurate diagnosis.
Using multiple diagnostic methods together can help healthcare providers understand the severity of the condition and tailor a treatment plan that works best for the patient. Early and accurate diagnosis is vital to prevent long-term damage and manage the patient’s condition effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, arthritis can be a painful and challenging condition, and early and accurate diagnosis is critical to managing it effectively. X-rays can provide healthcare providers with valuable information about the condition’s severity, but they are not the only tool used for diagnosis. A comprehensive approach, including a full medical history, physical exam, imaging, and laboratory tests, is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
If you suspect you may have arthritis, it’s essential to schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider. They can provide further information about the available diagnostic methods and recommend a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Understanding your condition and treatment options can help make the management of arthritis more manageable and comfortable.




