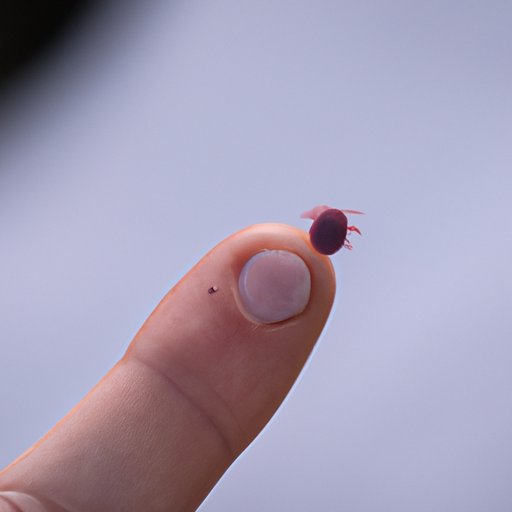
Introduction
While spending time outdoors may be a fun and relaxing activity, it is important to remain aware of the potential risks associated with exposure to ticks. Ticks can cause a variety of serious illnesses, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and others. If bitten by a tick, immediate antibiotic treatment may be necessary to prevent the onset of these diseases. In this article, we will explore the risks of tick bites and the importance of timely treatment.
Importance of Immediate Antibiotic Treatment after a Tick Bite
If left untreated, tick bites can lead to a variety of serious complications. Common symptoms include fever, chills, headache, and muscle aches, and can progress to more severe conditions if not recognized and treated promptly. In fact, some people develop chronic, long-term symptoms that can impact their quality of life for years to come.
The best way to prevent these complications is to recognize the symptoms of tick-borne diseases and seek prompt medical attention if you experience them. The earlier you begin antibiotic treatment, the more effective it will be in preventing the onset of these diseases.
Factors to Consider Before Taking Antibiotics after a Tick Bite
Antibiotics can be helpful in preventing the onset of tick-borne diseases, but they are not always necessary. It is important to consider the risks and benefits of antibiotics before beginning treatment. Factors such as the type of tick and the likelihood of infection should be considered before taking antibiotics, as well as any medical conditions or allergies you may have.
Home Remedies to Try Before Resorting to Antibiotics for Tick Bite Treatment
Some natural remedies can help alleviate symptoms associated with tick bites, including essential oils, aloe vera, and tea tree oil. Proper tick removal techniques are also essential to prevent infection and irritation. Finally, keeping a record of the bite and monitoring symptoms can help healthcare providers identify and treat any potential issues that arise.
The Science behind the Suggested 24-to-48-Hour Period to Begin Antibiotic Treatment
The timeframe for beginning antibiotic treatment after a tick bite is critical to its effectiveness. Antibiotics work by killing the bacteria that cause the infection, but they are only effective if begun within a certain timeframe. Studies have indicated that a window of 24-48 hours is ideal for beginning antibiotic treatment in order to prevent the onset of Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses.
Possible Consequences of Delaying Antibiotics for Too Long after being Bitten by a Tick
Untreated tick-borne diseases can lead to more severe complications, such as arthritis, nervous system disorders, and heart disease. Long-term effects on the body can include chronic fatigue, joint pain, and memory loss. Those with weakened immune systems are especially at risk of developing more severe symptoms from tick-borne illnesses.
How Proper Tick-Bite First Aid Could be More Beneficial Than Immediate Antibiotic Treatment
While antibiotics can be effective in preventing the onset of tick-borne diseases, proper tick-bite first aid can be more beneficial in the long run. This includes taking preventative measures to avoid tick bites, such as wearing protective clothing and using insect repellent. Proper first aid steps after a bite include cleaning the affected area thoroughly, removing the tick carefully, and monitoring symptoms. Antibiotics should only be administered if symptoms of a tick-borne illness develop.
Conclusion
Ticks can harbor a variety of serious illnesses that can cause long-term damage if not treated promptly. Therefore, it is important to recognize the symptoms of tick-borne diseases and seek immediate medical attention if you experience them. Remember to consider the risks and benefits of antibiotic treatment before beginning treatment, and try natural remedies and proper first aid before resorting to antibiotics. By remaining vigilant and aware of the risks of tick bites, you can take action to protect yourself and your loved ones from these dangerous illnesses.




